Recently, the American internet brokerage giant Robinhood announced the launch of "stock tokens" linked to equity in top private companies like OpenAI and SpaceX for European users, once again bringing the cutting-edge topic of tokenizing real-world assets (RWA) to the forefront. However, OpenAI quickly released an official statement, clearly stating that the tokens issued by Robinhood have no connection to the company and warned that "these tokens do not represent the company's actual equity."
This incident not only reveals the profound contradictions between financial innovation and traditional equity management but also provides a thought-provoking case for global regulators and market participants. The Crypto Law team will analyze the impact and significance of this case in conjunction with RWA-related explorations.

(Image source: 36Kr)
### 1. Background of the Incident
1. What is Robinhood?
At its core, we need to understand what kind of company Robinhood is. Robinhood Markets, Inc. is a financial services company based in Menlo Park, California, USA. The company is known for providing a stock app and website primarily aimed at retail investors. The services offered by Robinhood online are completely free. As a fintech company, Robinhood is dedicated to innovating financial products and service models.
Robinhood primarily offers trading in U.S. listed stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), related options, and cryptocurrencies, as well as cash management services. Its positioning is to provide commission-free trading services for ordinary retail investors in the U.S. for stocks, options, ETFs, and cryptocurrencies, and it generates profits mainly through interest income on customer cash balances, margin interest, and selling order flow to high-frequency trading firms.
It has established a European center in Lithuania and created an entity called Robinhood Europe UAB. According to public information, this entity has obtained an A-class financial brokerage license and a crypto asset service provider license issued by the Bank of Lithuania, allowing it to provide crypto asset custody, management, and trading services in Lithuania and the entire European Economic Area.
2. Summary of the Incident
The specific incident refers to Robinhood announcing at the European Crypto Finance Summit held in Cannes, France, the launch of a "stock token" product for users in the EU and the European Economic Area, allowing investors to trade over 200 U.S. stocks and ETFs around the clock in token form using blockchain technology. Among the most notable aspects is the tokenization of shares in the unlisted companies OpenAI and SpaceX, along with an airdrop of 5 euros worth of OpenAI tokens and SpaceX tokens to EU users as a reward to promote the product. Following this news, Robinhood's stock price surged significantly.
However, in the early hours of July 3, Beijing time, OpenAI released a statement on its official social media, clearly stating that these OpenAI tokens do not represent OpenAI's equity, that the company has not collaborated with Robinhood, has not participated in this matter, and does not endorse it, emphasizing that any transfer of OpenAI equity must be approved by the company, which has not approved any transfer. This news raises several questions:
What is this OpenAI token…?
Are the statements from Robinhood and OpenAI contradictory…?
What is the operational model and legal basis for Robinhood issuing OpenAI and SpaceX tokens…?
How does this incident differ from traditional RWA projects…?
The Crypto Law team will interpret these questions one by one.
(Image source: 36Kr)
### 2. Operational Model
1. What is the OpenAI Token?
First, the Crypto Law team will help everyone understand what the so-called "OpenAI token" actually is. This "OpenAI token" is essentially a tokenized contract on the blockchain linked to the shares held by Robinhood in a special purpose vehicle (SPV). Robinhood links the token price to the value of OpenAI shares in the SPV by holding shares in an SPV that controls a certain number of OpenAI shares.
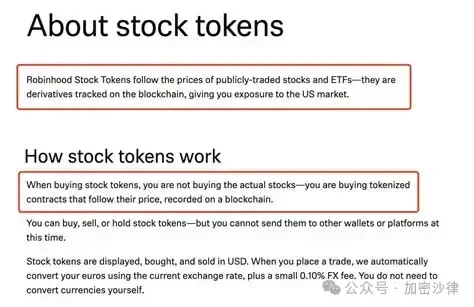
Therefore, the underlying asset of the OpenAI token is Robinhood's equity in the SPV it established. When users purchase the token, they are not buying actual OpenAI stock but rather a contract that follows its price and is recorded on the blockchain. There are two layers of separation between the token holders and the actual equity, and the price of the OpenAI token will fluctuate with the value of OpenAI shares in the SPV.
In other words, if OpenAI's valuation rises, the value of the shares in the SPV increases accordingly, the value of the SPV itself increases, and the value of Robinhood's shares in the SPV increases, then the price of the OpenAI token may also rise, and vice versa. Simply put, token holders have the right to gain corresponding profit from the price fluctuations of the relevant rights in the SPV, but do not own actual equity in OpenAI. This rule is written into the blockchain, and the token becomes a certificate for investors to hold this right.
2. Are the Statements from Both Parties Contradictory?
As can be seen from the above, the statements from Robinhood and OpenAI are not contradictory. OpenAI denies that the "OpenAI token" issued by Robinhood is not OpenAI's equity, emphasizes that it has not collaborated with Robinhood, has not participated in this matter, and does not endorse it. Any transfer of OpenAI equity must be approved by OpenAI, and it has not approved any transfers.
On the other hand, Robinhood also acknowledges that these tokens are not actual OpenAI equity but merely provide retail investors with indirect access to the private market through the equity held by Robinhood in the SPV. Therefore, both parties agree that the "OpenAI token" is not true equity of OpenAI; the dispute lies in whether Robinhood's issuance of this token is compliant and reasonable.
The operational model of Robinhood issuing the OpenAI token is as follows:
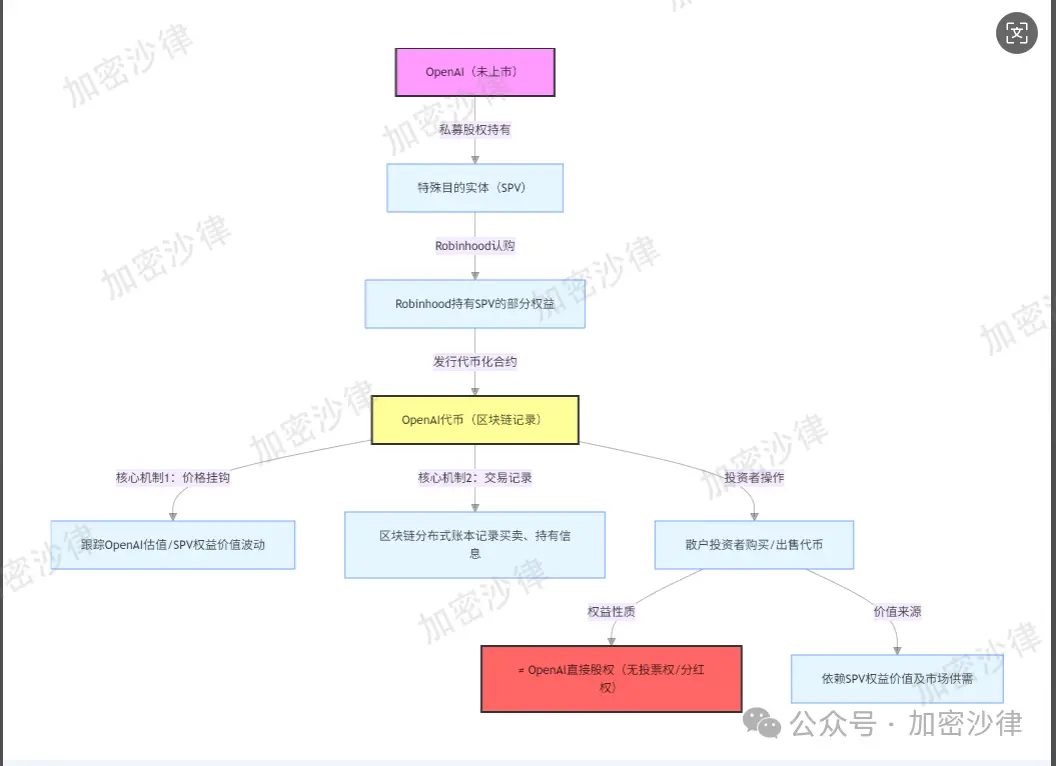
Returning to the statements from OpenAI and Robinhood, OpenAI denies that "token = equity," emphasizing that it has not authorized any equity-related products, which is consistent with the process where "token ≠ direct equity"; Robinhood acknowledges that the token is a "contract linked to price," consistent with the design of "indirectly linked to value through SPV" in the process. The point of contention between the two parties is whether "this indirect linkage is legal and compliant," rather than the factual description of the process itself.
3. Why Did Robinhood Issue This Token?
The "OpenAI token" launched by Robinhood is essentially an attempt at a "consensus asset": allowing ordinary investors to trade based on their judgment of OpenAI's future value through tokenization. This attempt addresses three major pain points in the current investment market:
First, the low accessibility of quality assets: top tech companies like OpenAI and SpaceX are not publicly listed, making it difficult for ordinary investors to share in their growth dividends.
Second, the high barriers to entry in traditional private equity and venture capital prevent ordinary retail investors from participating.
Finally, there is a surge in demand from investors for innovative assets: the explosive growth of alternative assets such as cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and meme stocks in recent years reflects a strong demand from investors for new narratives and new asset classes.
Against this backdrop, Robinhood aims to break the closed nature of the traditional financial system through tokenized trading, providing a new investment channel based on market consensus for a wide range of retail investors. Robinhood chose OpenAI because it is a leading company in the field of artificial intelligence, with extremely high market attention and influence.
By launching the OpenAI token, Robinhood can leverage its brand effect to attract investor attention and participation in trading. For example, by airdropping OpenAI tokens to EU users as rewards, it can effectively increase user registrations and trading volumes, enhance the company's visibility and market influence, and stimulate trading in other tokenized stock products.
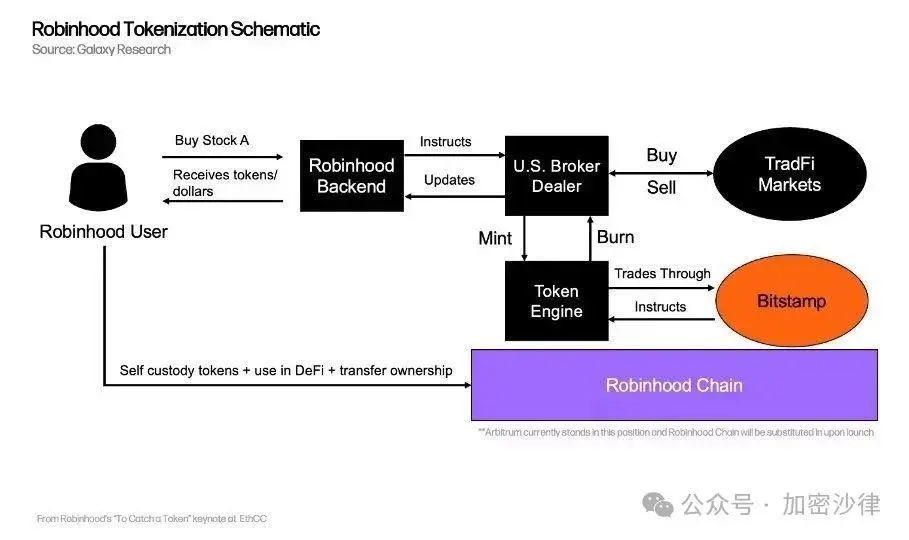
(Image source: Galoy Research)
4. Regulatory Authorities
Robinhood's issuance of the OpenAI token is currently subject to regulation by the Bank of Lithuania and the EU. Robinhood has obtained an A-class financial brokerage license and an EU crypto asset service provider license from the Bank of Lithuania, which is its lead regulatory authority within the EU. In response to Robinhood's issuance of the OpenAI token, the Bank of Lithuania has initiated an investigation, requiring Robinhood to provide details regarding the structure of the tokens, market promotion, and communication with consumers to assess their legality and compliance.
Robinhood's stock tokens are issued as derivatives under the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II). As trading volumes increase, it may also need to be regulated by ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority), and Robinhood must ensure compliance with relevant requirements such as prospectus disclosures. Currently, the token is only open to European citizens and has not been made available to U.S. citizens; if it later seeks to enter the U.S. market, it may also be subject to regulation by the SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission).
The reason Robinhood can issue the OpenAI token in Europe is primarily because:
Compared to the strict "qualified investor" system in the United States, the EU has relatively lower thresholds for retail investors to participate in complex financial product trading.
Robinhood's stock tokens, as derivatives, can be issued under the regulation of the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II), with their underlying assets held by licensed institutions in the U.S., thus meeting the EU's compliance requirements for financial products to some extent.
Robinhood provides services to retail investors in the EU through its application, and its cryptocurrency application in Europe has transformed into a more comprehensive investment platform.
### 3. Benefits and Risks for All Parties
1. Benefits and Risks for Investors
So, what benefits can investors and subscribers gain from this? What risks will they bear?
First, when professional investors subscribe to this OpenAI token, they gain an investment opportunity. Robinhood states that these tokens allow retail investors to indirectly access the private market, opening up investment access. By linking the price of the OpenAI token to the value of OpenAI shares represented by the SPV, subscribers theoretically have the opportunity to profit from the future valuation growth of OpenAI. If OpenAI performs well and its valuation rises, the price of the token may increase accordingly, allowing subscribers to gain profit by selling the tokens. This is the primary benefit that investors can reap.
Investors purchasing OpenAI tokens are not buying actual shares of OpenAI or shares in the SPV; instead, they are gaining an indirect exposure related to the price of OpenAI shares in the SPV. From a legal perspective, token holders do not possess voting rights, information rights, or other equity-related rights, nor do they have actual ownership of OpenAI or the SPV; they are more like holders of a "valuation tracker," able to gain profits or incur losses based on token price fluctuations.
However, this investment method also carries certain risks. OpenAI has publicly stated on social media platforms like Twitter that the token is not OpenAI's equity, and the company has not collaborated with Robinhood or endorsed it. This means that subscribers do not own actual equity in OpenAI, and cannot enjoy true shareholder rights such as voting rights or dividend rights, with their rights not being protected in the same way as holding real equity. In other words, based on the content released by OpenAI, investors seem to only be able to gain profits through the increase in OpenAI's equity value, and their status is not equivalent to that of shareholders.
Of course, investors also face value fluctuation and valuation risks when subscribing to this type of token. Although the token price is linked to the value of OpenAI shares held by the SPV, it may not accurately reflect OpenAI's actual value, potentially leading to significant discrepancies. Moreover, since OpenAI is a privately held company that is not publicly listed, its valuation inherently carries a high degree of uncertainty. If there are significant fluctuations in valuation, the token price may also fluctuate dramatically, exposing subscribers to substantial losses. Therefore, the Crypto Law team advises investors to carefully discern the risks involved, as the risk factor is much higher than that of traditional RWA projects.
2. Benefits and Risks for the Issuer
For the issuer Robinhood, the potential gains could be considerable.
First, the most immediate benefit is that after the announcement of this event, Robinhood's stock price surged by about 10%. This indicates that the market recognizes the innovative product it has launched, enhancing the company's market value and increasing shareholder equity, while also boosting the company's influence and visibility in the capital market. Additionally, the company can attract more investors to invest in its stock, thereby achieving its fundraising goals.
Furthermore, the potential benefit for Robinhood lies in its ability to capture market share and broaden its customer base through this event. The tokenized products launched by Robinhood target EU customers and lower the investment threshold, simplifying the complex KYC verification process.
Of course, Robinhood also bears certain risks.
In terms of market risk, the price of the OpenAI token is linked to the value of OpenAI shares in the SPV, and as OpenAI is a privately held company, its valuation is influenced by various factors such as technological development progress, effectiveness of business collaborations, and industry competition, leading to high volatility and uncertainty.
If OpenAI's valuation falls short of expectations or even declines, the value of the shares in the SPV will shrink, leading to a drop in the token price. This not only causes losses for investors but may also undermine market confidence in Robinhood's business, negatively impacting its brand reputation and overall business development.
Credit risk is also a significant concern. The OpenAI token is essentially a synthetic derivative, meaning that investors do not directly hold the underlying asset but gain economic exposure to price fluctuations through a contract. This implies that the realization of investors' rights is highly dependent on Robinhood's ability to fulfill its contractual obligations.
If Robinhood faces operational crises, fails to meet its contractual obligations, or even engages in fraudulent activities, it will directly harm investors' interests, triggering a trust crisis in the market and affecting its existing business and future expansion.
### 4. Differences Between This Project and Traditional RWA Projects
It is evident that the incident of Robinhood launching the OpenAI token differs in many aspects from traditional RWA (real-world asset) projects, as shown in Table 1:
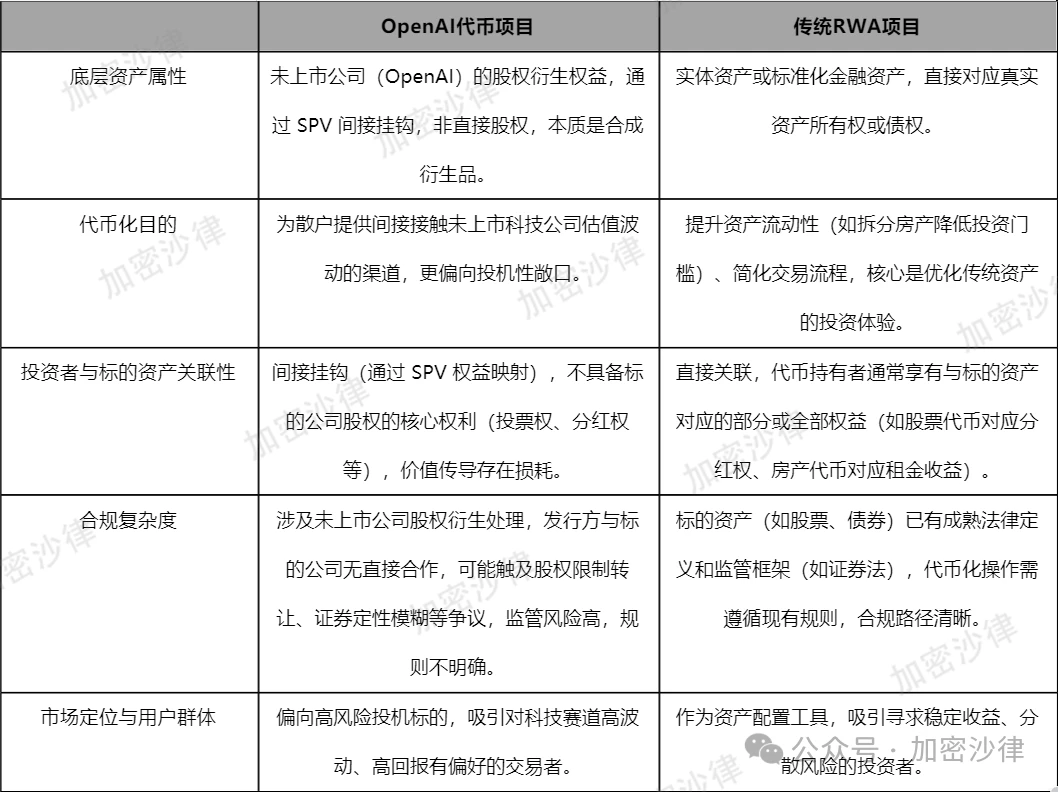
Table 1: Comparison of the OpenAI Token Project and Traditional RWA Projects
### 5. Crypto Law Interpretation
As a long-established brokerage, Robinhood has been exploring the cryptocurrency and digital asset space for years, with its launch of security token offerings (STO) in 2019 as an example. Previously, platforms like Gate and Bybit also attempted to develop U.S. stock tokenization businesses, launching some products on the compliance edge, but they did not attract widespread attention.
The strong reaction to Robinhood's issuance of the OpenAI token is primarily due to the core difference: while Gate and Bybit are institutions from the cryptocurrency space penetrating traditional finance, Robinhood is entering the cryptocurrency space as a traditional financial institution, leading to fundamentally different impacts on traditional finance. The audience of traditional financial institutions often lacks experience in the cryptocurrency space, and the Robinhood brand itself brings significant market influence.
Additionally, the investment targets of this project include tech giants like OpenAI and SpaceX, which have broad global influence, further attracting investors' attention to the concept of the "OpenAI token."
However, for institutions holding OpenAI stock, if one institution adopts tokenization, the interests of the other 19 institutions will be immediately harmed. Holding equal shares of stock, some institutions can implement such operations while others cannot, leading to a core issue of unilateral encroachment on interests, which will make it difficult for subsequent related operations to gain cooperation from other institutions.
For more institutions, if tokenization becomes a regular model, more investors will focus on stocks in the tokenized market, further increasing the volatility of stock prices and transforming the investment market into a place dominated by institutions with stronger speculative attributes. From the perspective of compliance practitioners, this model faces significant challenges. Tokens have a borderless nature, while listing rules have clear national boundaries, which will impact various global markets.
Secondly, the rigorous structure of the traditional financial system is maintained by company law, fund law, securities law, investor protection mechanisms, and exchange rules. However, token-related operations face numerous legal controversies, such as the ability to infinitely split tokens, which stocks cannot achieve; the registration system for stocks and internal filing systems have clear legal bases, and violations can be held accountable through internal mechanisms, while the free circulation of tokens on the blockchain is difficult to regulate and lacks proactive regulatory motivation, all of which significantly harm the interests of shareholders. Therefore, fundamentally, while Robinhood's issuance of the OpenAI token adds an investment target in the Web3 space, it does not create direct value for the stock market.
Although "stock tokenization" has drawbacks on certain levels and presents new challenges for investors, as an innovative initiative in the Web3 space, it has a certain degree of rationality. Web3 itself is a field that continuously breaks traditional logic, and the financial innovation exploration reflected in this event has certain positive significance. However, for practitioners in the traditional financial industry, the impact is quite strong. Therefore, both investors and other brokerages and companies interested in attempting "stock tokenization" should approach this event with caution.
This represents the personal views of the author and does not constitute legal advice or opinions on specific matters.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




