This report is written by Tiger Research. To achieve true autonomy in automation, native payment capability is essential. The market has already begun to actively prepare for this transition.
Key Points
- The payment entity is shifting from humans to AI Agents, making payment infrastructure a core requirement for achieving true autonomy.
- Big tech companies (including Google AP2 and OpenAI Delegated Payment) are designing automation payment systems based on approvals on top of existing platform infrastructure.
- Cryptocurrencies have achieved a disintermediated payment model through ERC-8004 and x402 standards, utilizing NFT-based identity recognition and smart contracts.
- Big tech companies prioritize convenience and consumer protection, while cryptocurrencies emphasize user sovereignty and broader Agent-level execution capabilities.
- The key question for the future is: Will payment be controlled by platforms or executed by open protocols?
1. Payment is no longer exclusive to humans
Source: macstories (Feder1C0 Viticci)
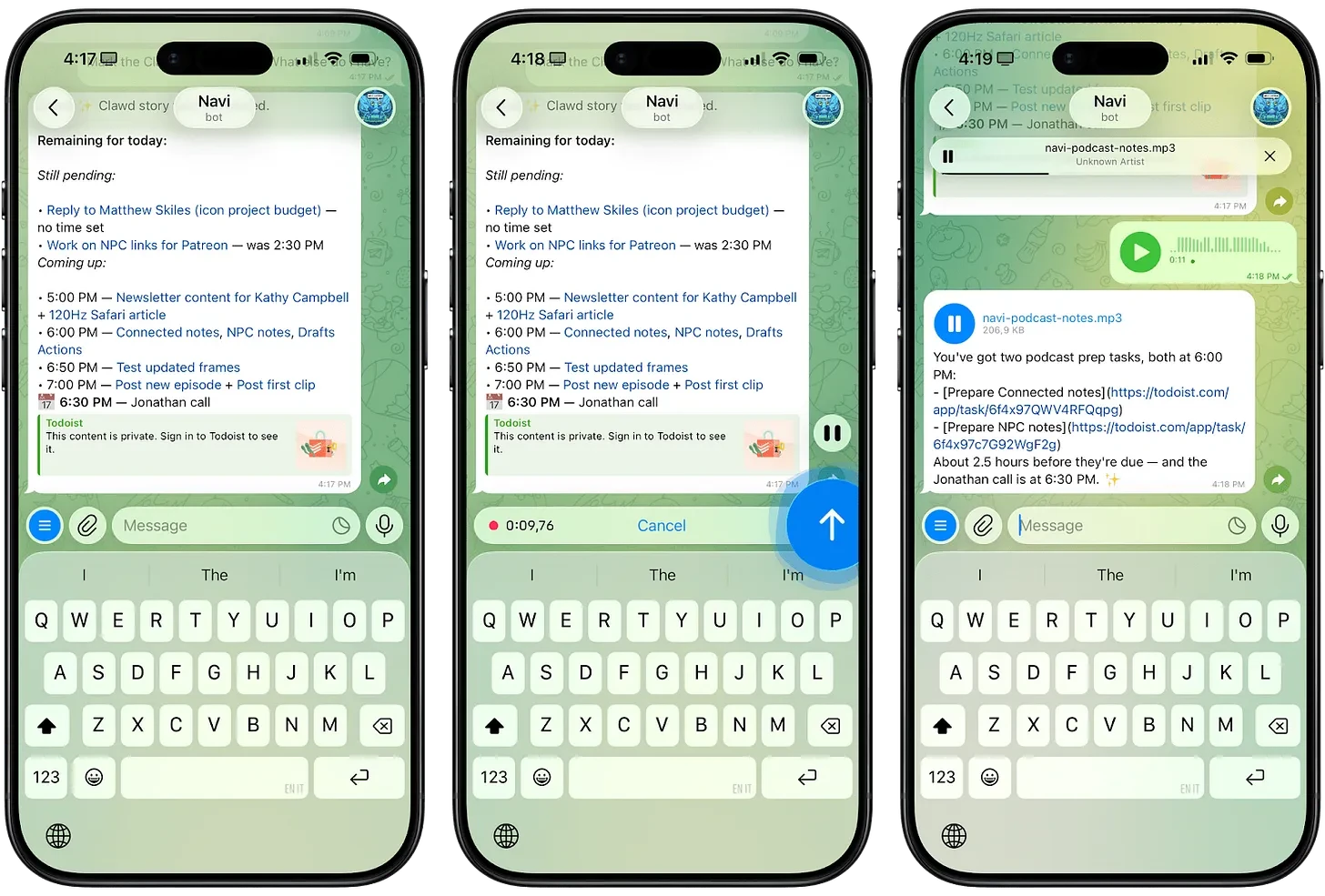
Recently, “OpenClaw” has attracted widespread attention. Unlike major AI systems like ChatGPT or Gemini that are mainly responsible for retrieving and organizing information, OpenClaw allows AI Agents to execute tasks directly on the user's local PC or server.
Through instant messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Slack, users can issue commands, and the Agent subsequently independently executes tasks, including email management, calendar coordination, and web browsing.
Since it operates as open-source software and is not tied to a specific platform, OpenClaw functions more like a personal AI assistant. This architecture is favored for its flexibility and user-level control.
However, a key limitation still exists. For AI Agents to achieve complete autonomy, they must be able to execute payments. Currently, Agents can search for products, compare options, and add items to carts, but the final payment authorization still requires human approval.
Historically, payment systems have been designed around human subjects. In an AI Agent-driven environment, this assumption no longer holds. If automation is to become fully autonomous, Agents must be able to independently assess, authorize, and complete transactions within defined constraints.
Anticipating this shift, large tech companies and native crypto projects have introduced technological frameworks aimed at achieving Agent-level payments over the past year.
2. Big Tech Companies: Agent Payments Built on Existing Infrastructure
In January 2025, Google launched AP2 (Agent Payment Protocol 2.0), expanding its AI Agent payment infrastructure. While OpenAI and Amazon have also outlined relevant initiatives, Google is currently the only large enterprise with a structured implementation framework.
AP2 divides the transaction process into three Mandate Layers. This structure allows for independent monitoring and auditing at each stage.
- Intent Mandate: Records the action the user wishes to execute.
- Cart Mandate: Defines how to execute the purchase under preset rules.
- Payment Mandate: Executes the actual transfer of funds.
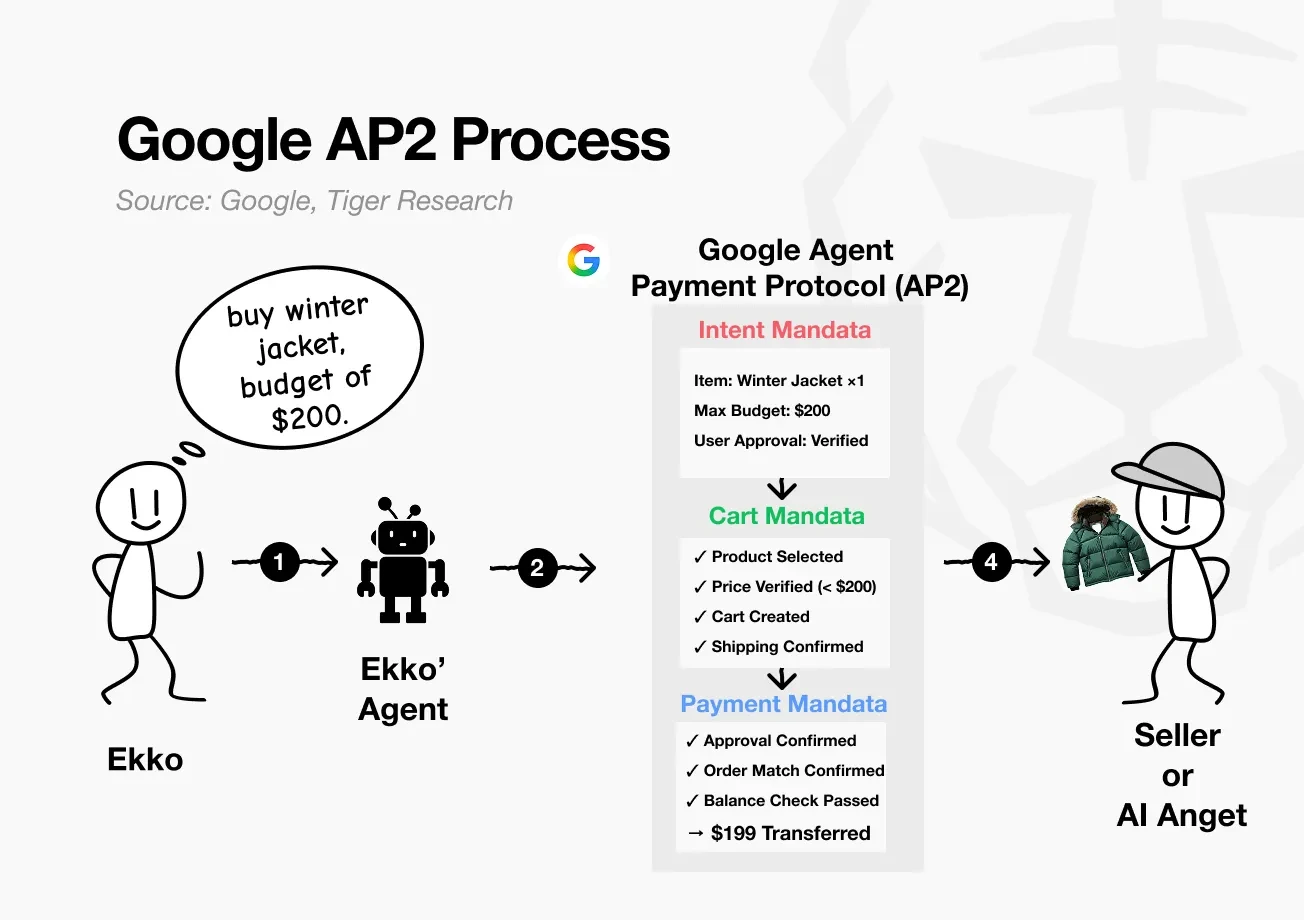
Example: Suppose Ekko instructs the AI Agent on Google Shopping to “find and purchase a winter jacket under $200.”
- Intent Mandate: Ekko instructs the AI Agent to purchase “a winter jacket with a maximum budget of $200.” This information is recorded on the chain as a digital contract, namely the intent mandate.
- Cart Mandate: The AI Agent follows the intent, searches for matches among partner merchants, and adds eligible items to the cart. Verify price ($199, within budget ✓), confirm shipping address.
- Payment Mandate: Ekko reviews the selected items and clicks approve. $199 is processed through Google Pay. Alternatively, the AI Agent may automatically complete the payment within preset parameters.
Throughout the process, the user does not need to input any additional information. Google AP2 relies on existing user credentials (pre-registered cards and addresses), reducing the entry barrier and simplifying the adoption process.

Source: Google
However, Google currently only supports Agent payments within its partner network. Therefore, its usage scope is limited to a controlled ecosystem, restricting broader interoperability and open access.
3. Cryptocurrencies: Self-Custody and Open Exchange
The crypto space is also developing payment infrastructure for AI Agents, but its approach is fundamentally different from that of big tech companies. Large platforms establish trust within a controlled ecosystem, while the crypto space starts from another question: Can AI Agents gain trust without relying on centralized platforms?
Two core standards aim to address this goal: Ethereum's ERC-8004 and Coinbase's x402.
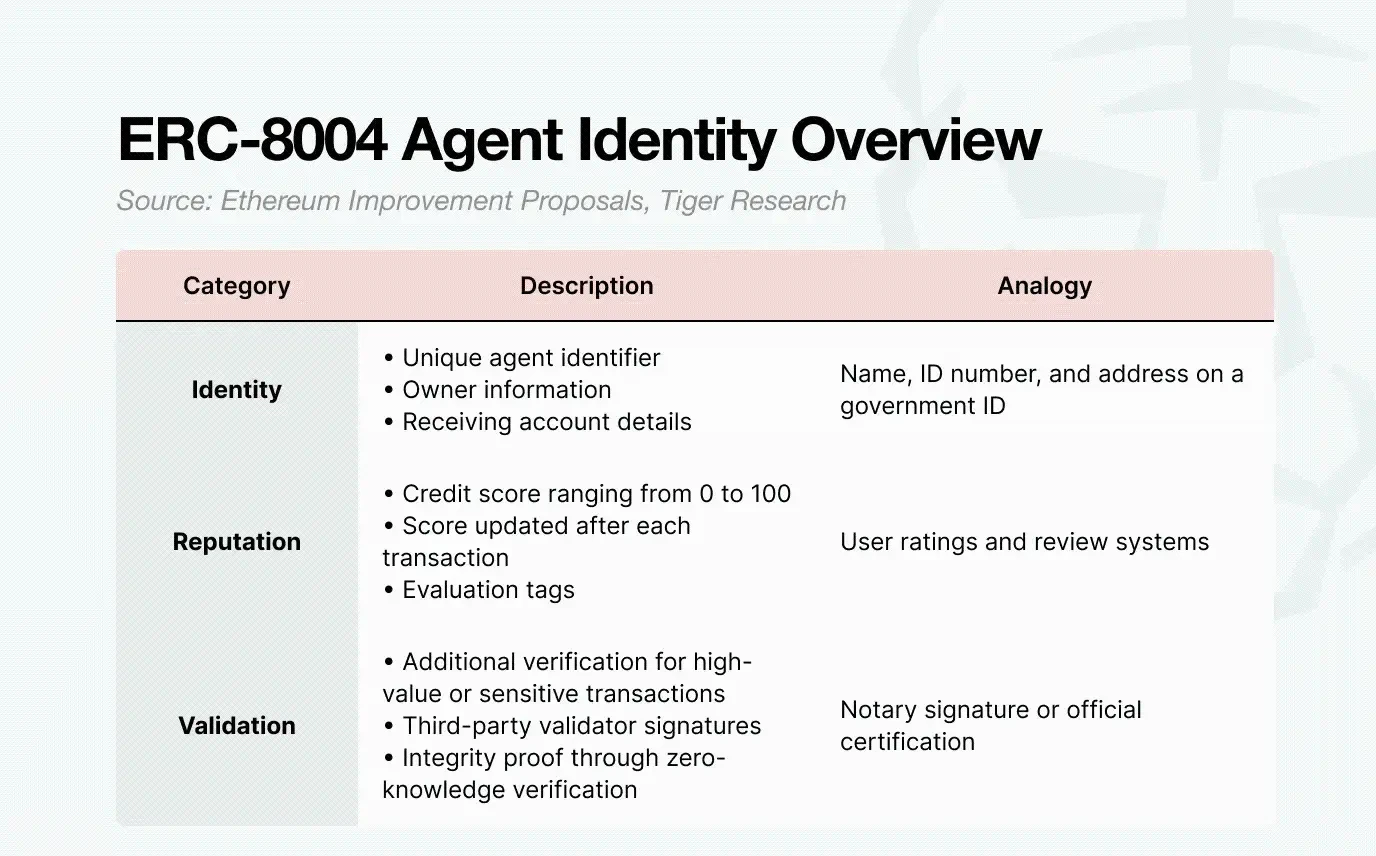
First is the identity layer. AI Agents run on the blockchain must be identifiable. ERC-8004 serves this function. It is issued in NFT form, but not as art collectibles, rather as credential NFTs containing structured identity data. Each Token contains three parts:
- Identity
- Reputation
- Validation
These elements together constitute a verifiable on-chain identity certificate.
In terms of payment mechanisms, x402 serves as the payment pathway. Developed by Coinbase, x402 is the crypto-native payment standard for AI Agents. It enables Agents to conduct autonomous transactions using stablecoins. Its core feature is automated smart contract execution, where conditional logic is directly embedded in the code, allowing for settlement without human intervention once conditions are met.
When ERC-8004 (identity) combines with x402 (payment), AI Agents can verify counter-parties and execute transactions without relying on centralized platforms.
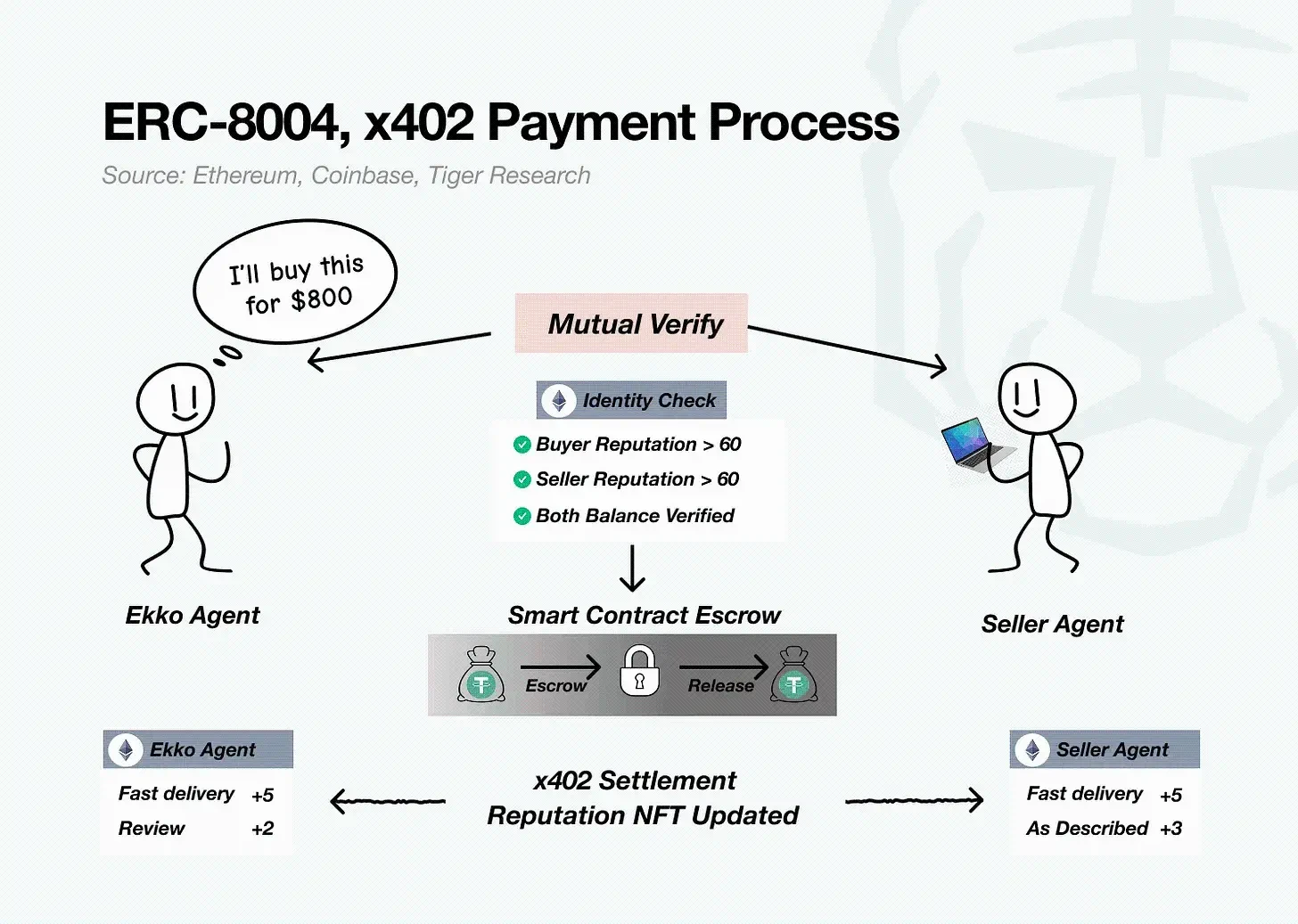
Example: Ekko instructs his Agent A to purchase a second-hand laptop with a maximum budget of $800. The seller's Agent B communicates directly with it.
- Mutual Verification: Check identity and reputation scores via the ERC-8004 NFT (e.g.: reputation 72, balance confirmed).
- Smart Contract Escrow: $800 transferred from the wallet to a smart contract escrow, locked until receipt is confirmed.
- Settlement and Reputation Update: After the transaction is completed, x402 automatically settles, and both parties' reputation records are automatically updated and written into their respective ERC-8004 NFTs.
Throughout the process, no intermediaries are involved. The two AI Agents conduct transactions directly through blockchain-based verification and settlement, exemplifying the Agent-to-Agent (A2A) business's crypto-native model.
4. Big Tech vs Cryptocurrencies: Differences in AI Agent Operational Domains
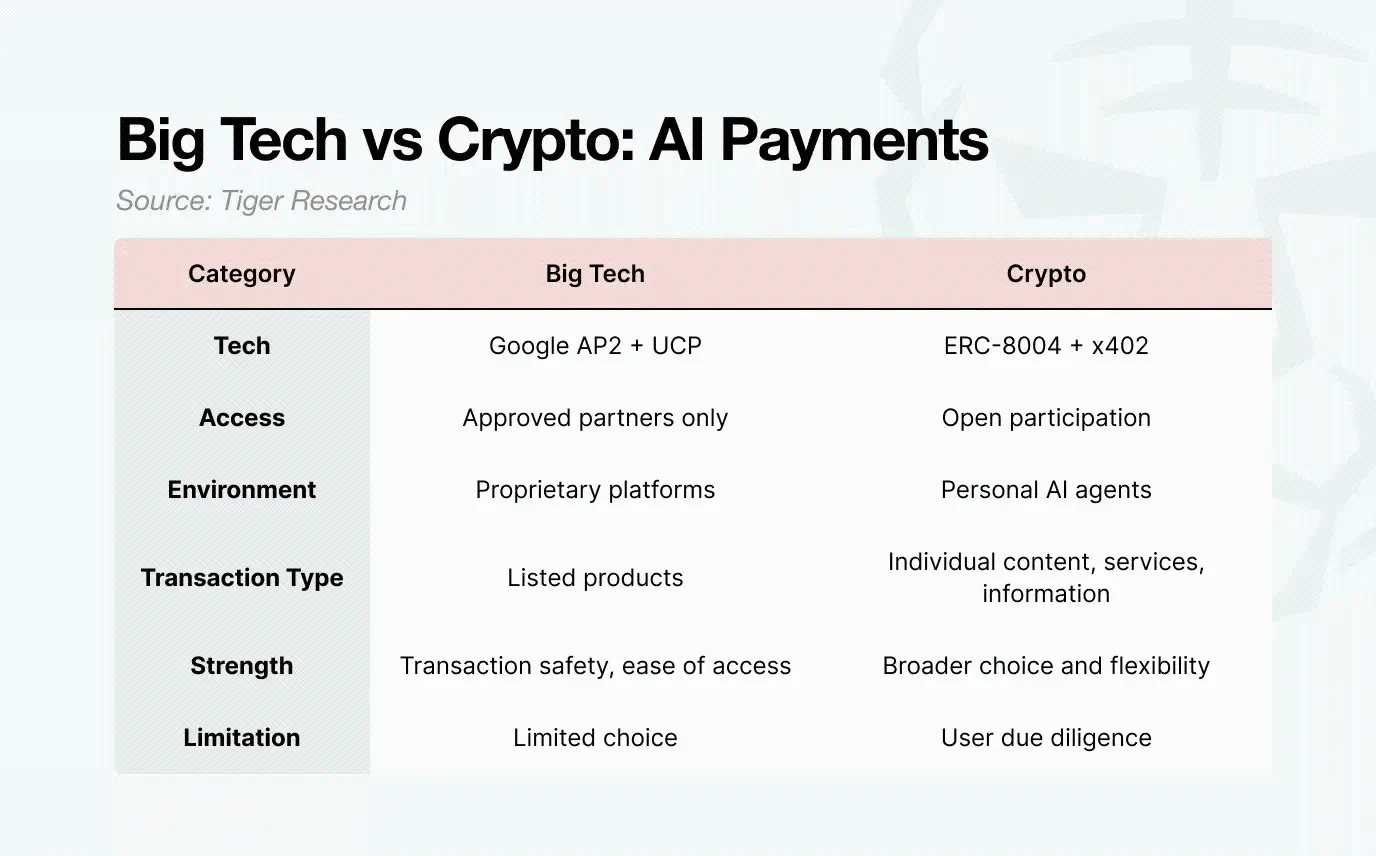
Google AP2 represents a controlled model designed for verified partners. Google restricts market participants to protect consumers. Since the execution of AI Agents has probabilistic outcomes rather than complete certainty, if a transaction error occurs, liability may ultimately fall on the payment infrastructure provider. To reduce the probability of failure, Google is motivated to narrow its ecosystem.
The restricted ecosystem increases stability but also limits the Agents' ability to operate autonomously and optimize choices in a broader market.
In contrast, ERC-8004 and x402 reflect a more open architecture. The crypto model is designed to achieve permissionless and interoperable systems.
While end-to-end execution may not currently be perfect, the long-term vision is for Agents to independently manage everyday expenditures. Large platforms may attempt to integrate major retail channels, while open crypto standards have structural advantages in handling small, high-frequency programmatic payments (micropayments). For example, an Agent purchasing 1,000 stock images at $0.01 each would experience higher operational efficiency through crypto-native paths.
Of course, the absence of centralized entities also brings trade-offs: identity assessment standards must be established in a decentralized manner, and no single entity bears ultimate responsibility for failures.
Conclusion
Both big tech companies and the crypto space pursue the same goal: achieving autonomous AI Agent commerce. The difference lies in the architecture: big tech companies favor closed, controlled systems while the crypto space advances open, protocol-based models.
The future trend is more likely to be interoperability between the two approaches, rather than a zero-sum game.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




