作者 | @arndxt_xo
编译 | Odaily 星球日报(@OdailyChina)
译者 | 叮当(@XiaMiPP)
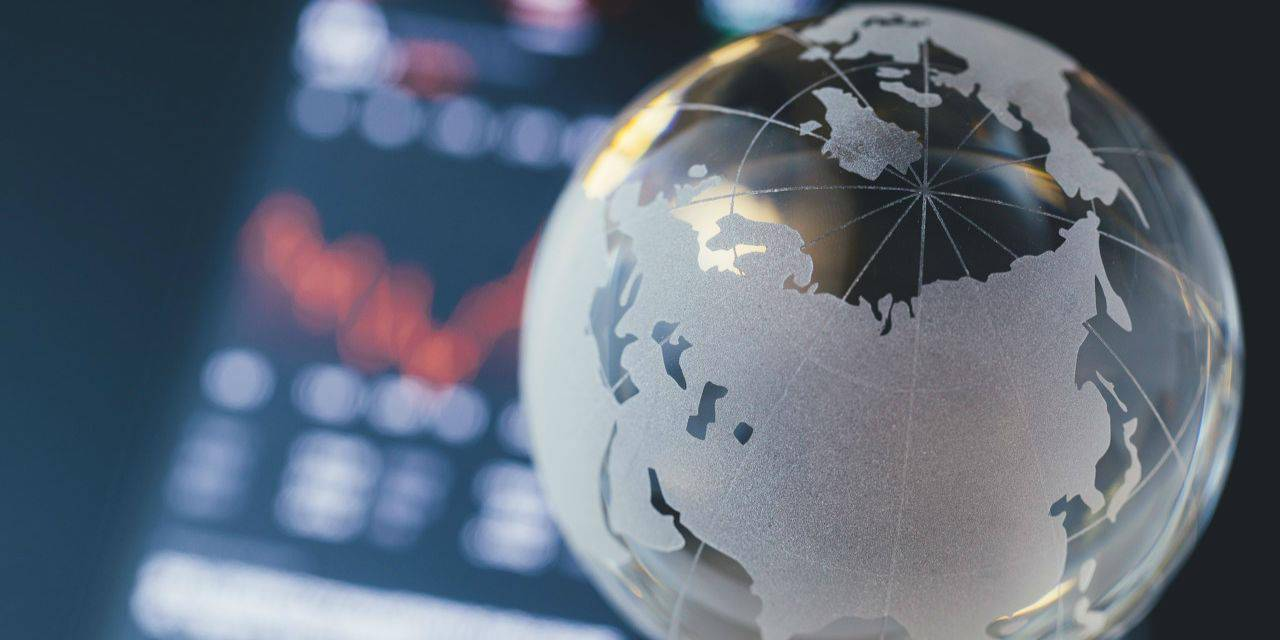

大幅回调与量化宽松(QE)周期相吻合—,当美联储有意延长其持有资产的到期日,以压低长期收益率(这项操作被称为“扭转操作”(Operation Twist)以及 QE2/QE3 )。
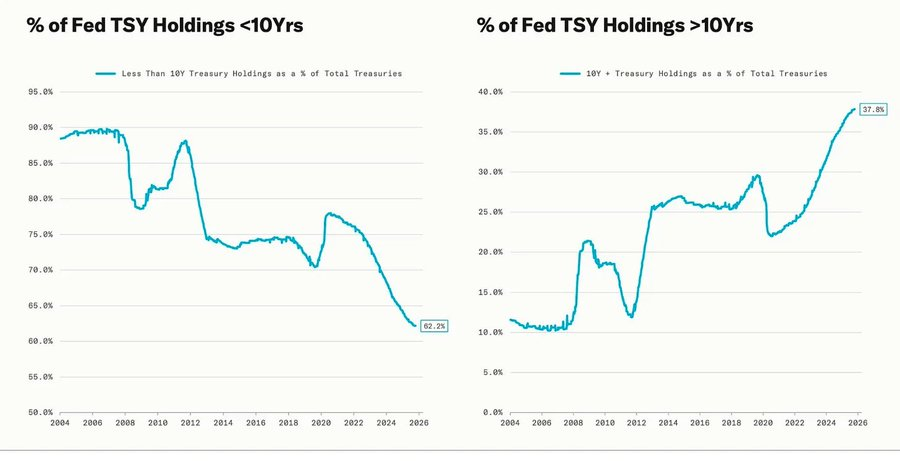
鲍威尔的“在雾中驾驶”隐喻,已不再局限于美联储本身,而是成为当今全球经济的写照。无论是政策制定者、企业,还是投资者,都在缺乏清晰视野的环境中摸索前行,只能依赖流动性反射与短期激励机制。
新的政策体制呈现出三个特征:能见度有限、信心脆弱、流动性驱动的扭曲。
美联储的“鹰派降息”
此次 25 个基点的“风险管理式”降息,将利率区间降至 3.75%–4.00%,与其说是宽松,不如说是“保留选择权”。
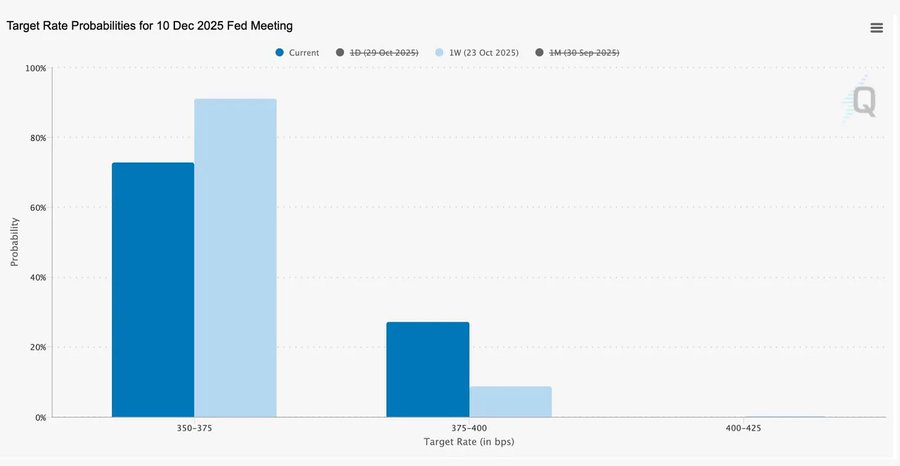
由于存在两种截然相反的的意见,鲍威尔向市场传递了明确信号:“放慢脚步——能见度已经消失”。
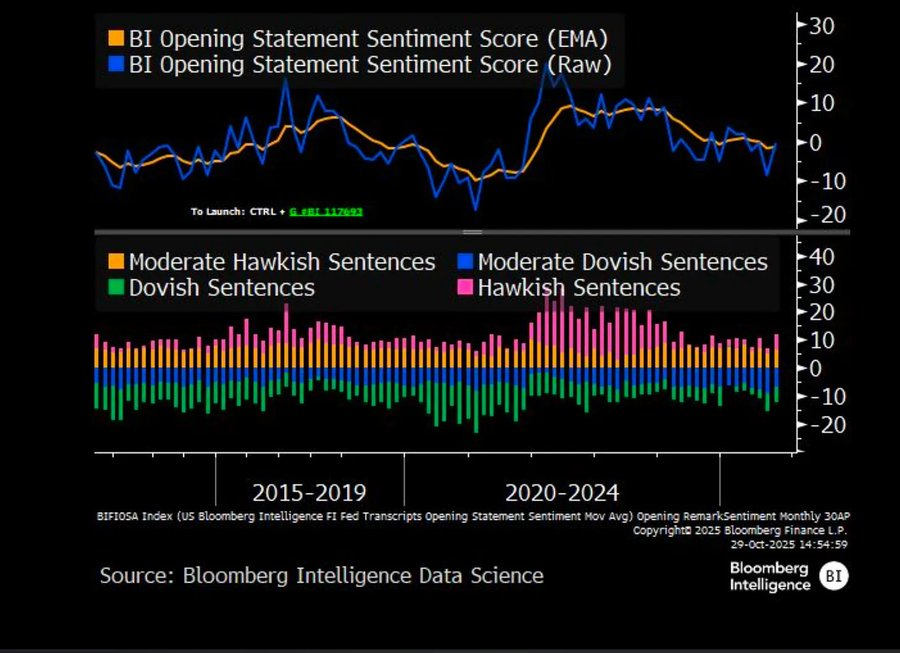
由于政府停摆引发的数据空白期,美联储几乎是在“盲开”。鲍威尔对交易员的暗示非常清楚:12 月能否公布利率尚无定论。降息预期迅速回落,短端利率曲线趋平,市场正在消化从“数据驱动”转向“数据缺失”的谨慎。
2025:流动性“饥饿游戏”
央行反复的干预措施使投机行为制度化。如今,决定资产表现的不是生产力,而是流动性本身——这种结构导致估值不断膨胀,而实体经济的信贷却在走弱。
讨论进一步扩展至对当下金融体系的清醒审视:被动集中、算法自反、散户期权狂热——
- 被动资金与量化策略主导流动性,波动率由仓位决定,而非基本面。
- 散户的看涨期权买盘与 Gamma 挤压在“Meme 板块”中制造出合成价格动能,而机构资金则扎堆涌向愈发狭窄的市场领头股。
- 主持人将这一现象称为“金融版饥饿游戏”——一个由结构性不平等与政策自反性塑造的体系,迫使小投资者走向投机性生存主义。
2026 展望:资本开支的繁荣与隐忧
AI 投资浪潮正推动“大科技”进入一种后周期的工业化阶段——当下靠流动性驱动,未来则面临杠杆敏感风险。
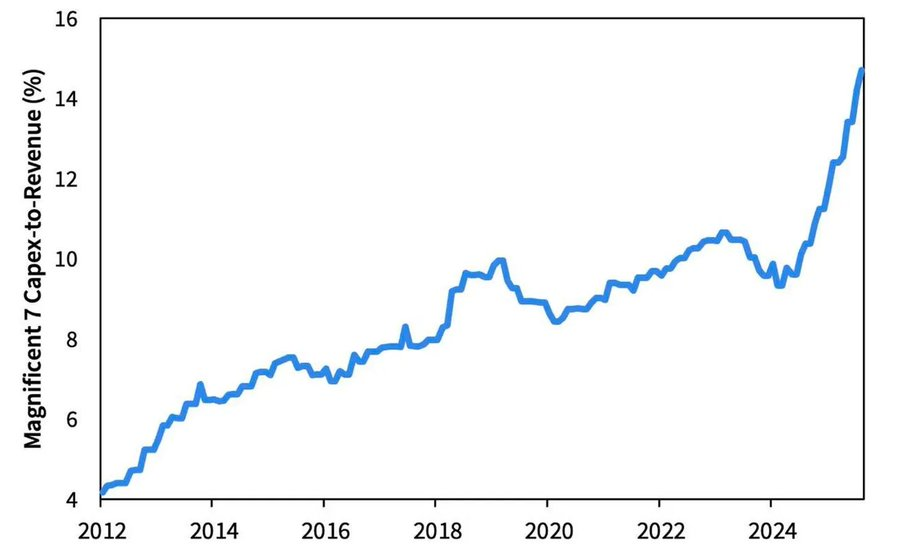
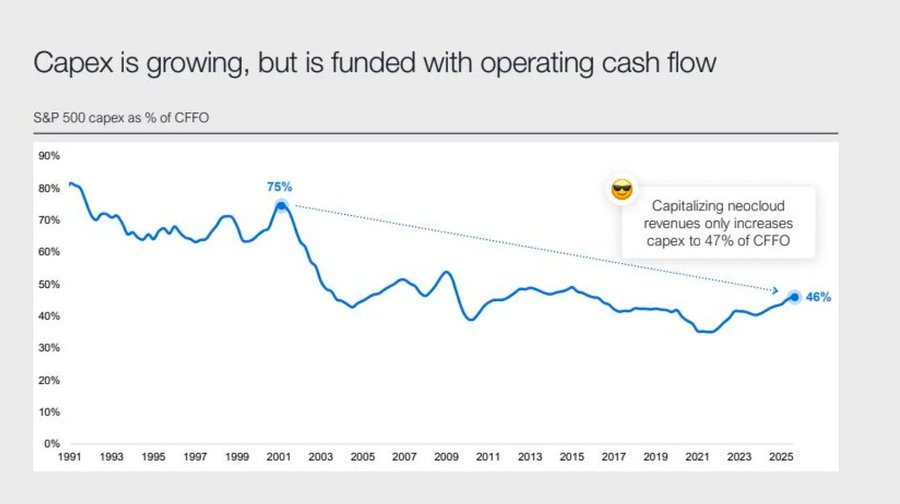
企业盈利依然亮眼,但底层逻辑正在转变:曾经的“轻资产现金机器”正在转型为重资本基础设施玩家。
- AI 与数据中心的扩张,初期依靠现金流,如今则转向创纪录的债务融资——例如 Meta 超额认购的 250 亿美元债券。
- 这一转变意味着利润率受压、折旧攀升、再融资风险上升——为下一轮信用周期的转向埋下伏笔。

结构性评论:信任、分配与政策循环
从鲍威尔的谨慎语气到最后的反思,一条清晰主线贯穿始终:权力集中化与信任流失。
政策的每一次救助,几乎都在强化最大的市场参与者,使财富进一步集中、市场完整性持续削弱。美联储与财政部的协调操作——从量化紧缩(QT)转向短期国债(Bill)购买——加剧了这种趋势:流动性充裕在金字塔顶端,而普通家庭却被停滞的工资与攀升的债务压得喘不过气。
如今最核心的宏观风险已不再是通胀,而是制度疲劳。市场表面依旧繁荣,但对“公平与透明”的信任正在流失——这,才是 2020 年代真正的系统性脆弱所在。
宏观周报 | 2025 年 11 月 2 日更新
本期涵盖以下内容:
- 本周宏观事件
- 比特币热度指标
- 市场概览
- 关键经济指标
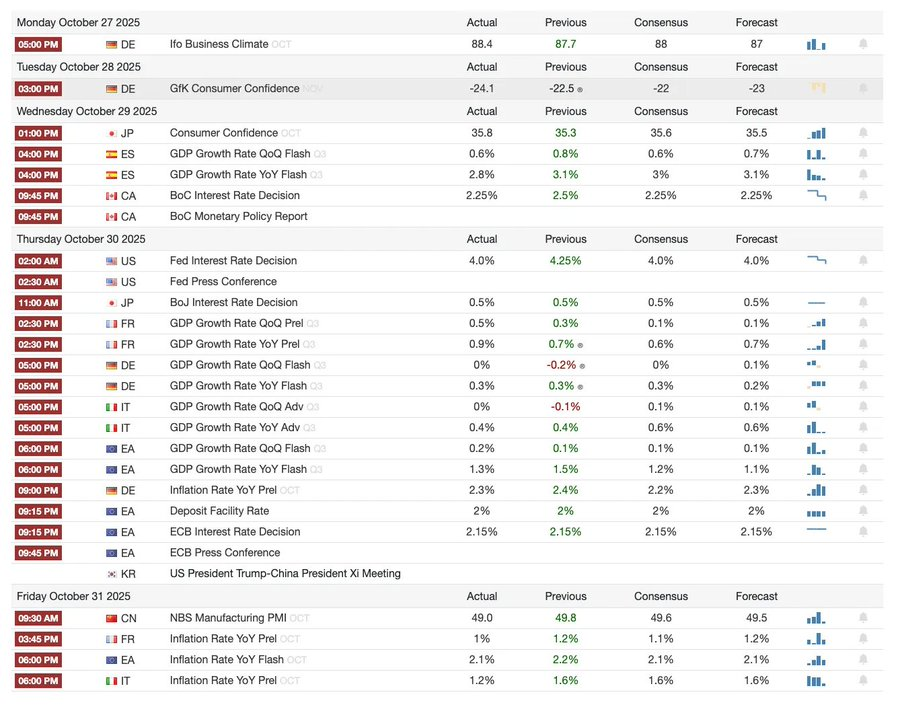
本周宏观事件
上周
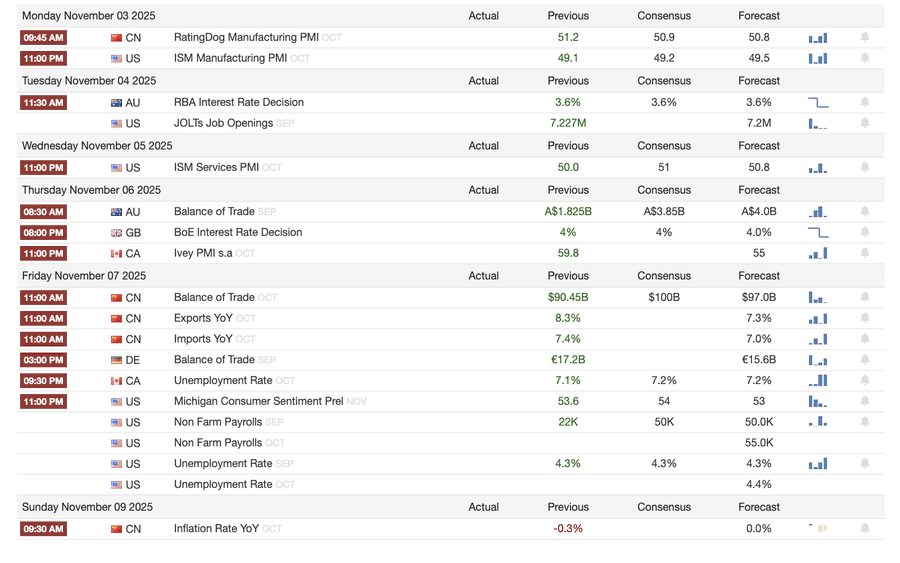
下周

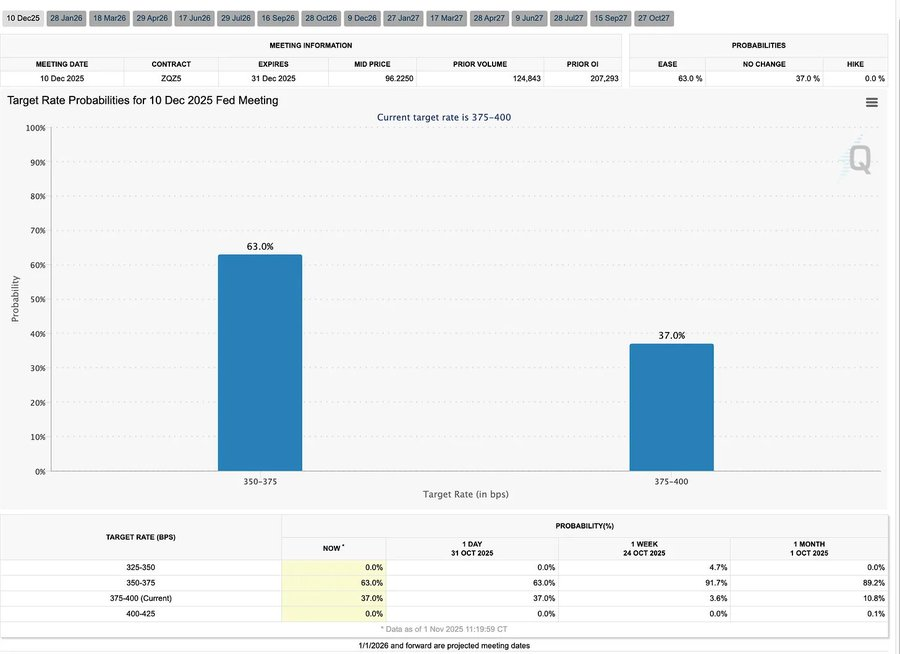
比特币热度指标
市场事件与机构动态
- Mt. Gox 将偿还期限延长至 2026 年,约 40 亿美元比特币仍被冻结。
- Bitwise Solana ETF 首周管理规模达 3.389 亿美元,刷新纪录,即便 SEC 仍处于审批僵局。
- ConsenSys 计划于 2026 年 IPO,承销商包括摩根大通与高盛,目标估值 70 亿美元。
- 特朗普媒体集团 推出 Truth Predict ——首个由社交媒体平台与 Crypto.com 合作的预测市场。
金融与支付基础设施升级
- 万事达(Mastercard) 以最高 20 亿美元 收购加密基础设施初创公司 Zerohash。
- 西联汇款(Western Union) 计划于 2026 年在 Solana 上推出稳定币 USDPT,并注册 WUUSD 商标。
- 花旗银行与 Coinbase 联手推出机构级 24/7 稳定币支付网络。
- Circle 发布 Arc 公测网,吸引 包括贝莱德与 Visa 在内的 100 多家机构参与。
生态与平台扩张
- MetaMask 推出多链账户,支持 EVM、Solana,并即将上线比特币支持。
全球与地区动态
- 吉尔吉斯斯坦 推出以 BNB 作为抵押的稳定币;同时,特朗普特赦 CZ,为币安重返美国市场铺平道路。
- 美国 SOL 现货 ETF(不含种子资金)流入 1.992 亿美元。
- 日本推出完全合规的日元稳定币 JPYC,目标到 2028 年发行规模 650–700 亿美元。
- 蚂蚁集团注册“ANTCOIN”商标,低调重返香港稳定币赛道。
- AWS 与微软云服务中断,引发市场混乱,双方说法相互矛盾。
- 摩根大通 Kinexys 区块链完成首个私募股权基金代币化交易,进一步推动机构采用。
- Tether 成为主要的美国国债持有者之一,持仓达 1350 亿美元,年化收益超 100 亿美元。
- Metaplanet 启动股票回购计划,以应对净资产下滑。
- 隐私资产交易热度上升,ZEC 价格突破 2021 年高点,但本周涨幅仍落后于 DASH。
- Sharplink 在 Linea 上部署 2 亿美元 ETH,以获取 DeFi 收益。
- 随着体育博彩成为热门板块,Polymarket 计划于 11 月底在美国正式推出产品。
- Securitize 宣布将通过 12.5 亿美元 SPAC 合并上市。
- Visa 新增对四种稳定币、四条链的支付支持。
- 21Shares 递交 Hyperliquid ETF 申请,更多加密基金正在进入市场。
- KRWQ 成为首个在 Base 链 上发行的韩元稳定币。
市场概览
全球经济正从通胀风险向信心风险过渡——未来的稳定性将取决于政策的清晰度,而非流动性。
全球货币政策正步入能见度受限的阶段。在美国,FOMC 将利率下调 25 个基点至 3.75%–4.00%,暴露出内部分歧扩大。鲍威尔暗示未来进一步宽松“并非板上钉钉”。持续的政府停摆使决策者无法获取关键数据,加剧政策误判风险。消费者信心减弱、房地产放缓,意味着市场情绪而非刺激措施,正在左右经济“软着陆”的走向。
在 G10 国家中:加拿大央行完成最后一次降息、欧洲央行维持 2.00% 利率不变、日本央行谨慎暂停。各方共同面对的难题是:在持续的服务业通胀背景下,如何抑制经济增长。与此同时,中国 PMI 再度跌回收缩区间,显示复苏乏力、民间需求低迷、政策疲态显现。
叠加政治风险,美国政府停摆威胁到福利项目的正常运作,并可能延迟关键数据发布,从而削弱财政治理的信心。债券市场已经开始消化收益率下降和经济增长放缓的预期,但真正的风险在于制度反馈机制的瓦解——数据延迟、政策犹豫不决和公众信任度下降三者交织在一起,最终酿成危机。
关键经济指标
美国通胀:温和回升,路径更清晰
通胀回升主要由供给推动,而非需求拉动。核心压力仍受控,就业动能减弱,使美联储有空间在不引发通胀反弹的情况下继续降息。
- 9 月通胀 同比 3.0%、环比 0.3%,为今年 1 月以来最快,但仍低于预期,强化了“软着陆”叙事。
- 剔除食品与能源的核心 CPI 同比 3.0%、环比 0.2%,显示价格基础稳定。
- 食品价格上涨 2.7%,其中肉类上涨 8.5%,受移民限制引发的农业劳动力短缺影响。
- 公用事业成本显著上升:电价 +5.1%,天然气 +11.7%,主要受 AI 数据中心能耗拉动——通胀的新驱动因素。
- 服务业通胀降至 3.6%,为 2021 年以来最低,表明劳动力市场降温正在缓解薪资压力。
- 市场反应积极:股市上涨,利率期货强化降息预期,债券收益率整体持稳。
美国人口结构:临界性转折
净移民转负,经济增长、劳动力供给与创新能力均面临挑战。
美国或将迎来一个世纪以来的首次人口下降。尽管出生数仍高于死亡数,但净移民为负,抵消了 2024 年的 300 万人口增量。美国正面临人口结构逆转,而这并非由生育率下降所致,而是由政策导致的移民锐减所致。短期影响包括劳动力短缺和工资上涨;长期风险则集中在财政压力和创新放缓。除非扭转这一趋势,否则美国可能会重蹈日本老龄化覆辙——经济增长放缓、成本上升,并面临结构性生产力挑战。
根据 AEI 预测,2025 年净迁移 –52.5 万人,为现代史首次负值。
- 皮尤研究中心数据显示,2025 年上半年外国出生人口减少 150 万人,主因是驱逐出境与主动离境。
- 劳动力增速停滞,农业、建筑、医疗等行业面临明显短缺与薪资压力。
- 28% 的美国青年为移民或移民子女,若移民归零,18 岁以下人口或将在 2035 年下降 14%,养老金与医疗负担将加剧。
- 医生中 27%、护理助理中 22% 为移民,若供给下滑,医疗行业自动化与机器人化可能加速。
- 创新风险:移民曾贡献 38% 的诺贝尔奖 与约 50% 的十亿美元级初创企业,若趋势逆转,美国创新引擎将受损。
日本出口回升:在关税阴影下的复苏
尽管受到美国关税拖累,日本出口仍出现反弹。9 月出口同比增长 4.2%,为 4 月以来首次正增长,主要来自亚洲与欧洲需求回暖。
经过数月萎缩后,日本出口恢复增长,9 月份同比增长 4.2%,创 3 月份以来最大增幅。这一反弹凸显了尽管与美国出现新的贸易摩擦,但区域需求依然强劲,供应链也已做出相应调整。
日本的贸易表现表明,尽管美国对汽车(其核心出口类别)加征关税,但亚洲和欧洲的外部需求已初步企稳。进口回升则表明,在日元走软和补库存周期的推动下,内需则出现温和反弹。
前景:
- 预计在亚洲内部供应链和能源价格正常化的带动下,出口将逐步复苏
- 美国持续的保护主义仍然是 2026 年维持出口势头的主要阻力。
相关阅读《为什么说即将到来的量化宽松是泡沫制造机?》
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




